Resumen
¿Qué es un DNS?
DNS stands for "Domain Name System", and its purpose is to convert website names into IP addresses. Each time you go to a website, your browser sends a DNS query to a DNS server to figure out the IP address of the website. And a regular DNS resolver simply returns the IP address of the requested domain.
The default DNS server is usually provided by your ISP. This means that your ISP can track your online activity and sell logs to third parties.
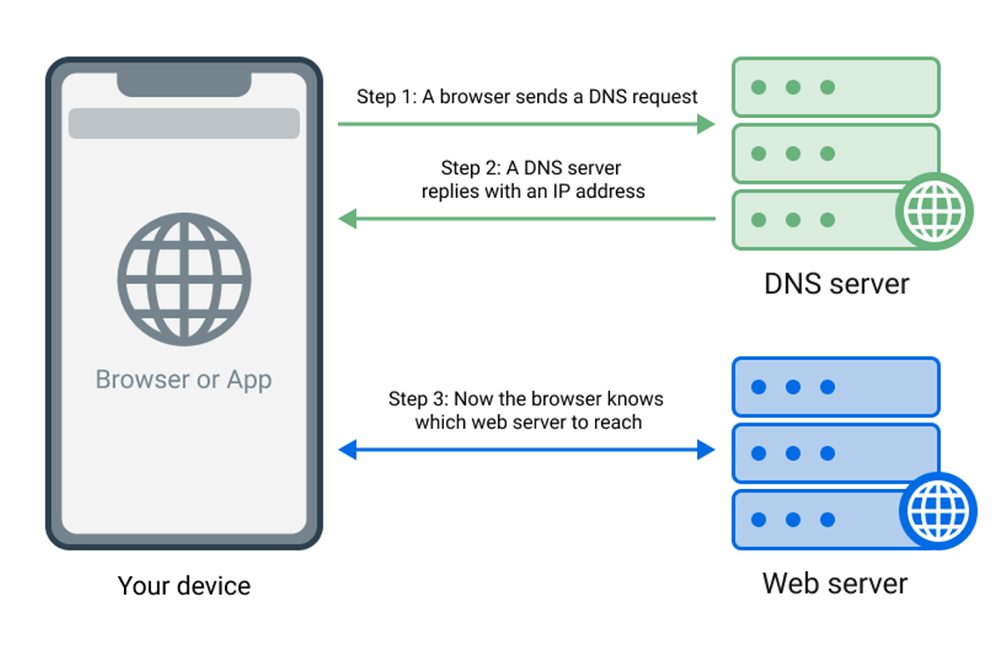
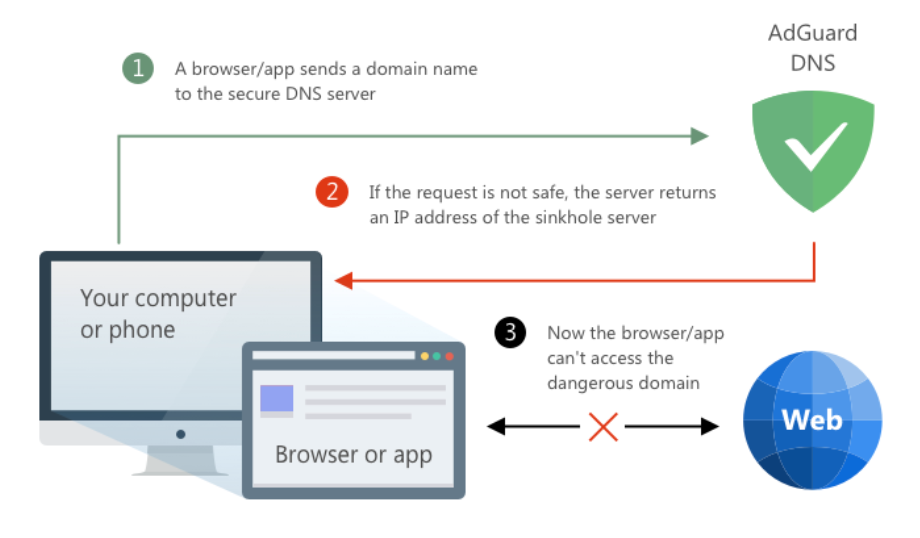
There are also DNS servers that can block certain websites at DNS-level. How do they work? When your device sends a "bad" request, be it an ad or a tracker, a DNS server prevents the connection by responding with a non-routable IP address for a blocked domain.
Why use DNS for content blocking
Absolutely everything is connected to the Internet these days, from TV to smart light bulbs, from mobile devices to smart car. And where the Internet is, there are ads and trackers. In this case, a browser-based ad blocker has proven insufficient. To get a better protection, use DNS in combination with VPN and ad blocker.
Using DNS for content blocking has some advantages as well as obvious flaws. On the one hand, DNS is in the loop for queries from all devices and their apps. But, on the other hand, DNS blocking alone cannot provide cosmetic filtering.
What is AdGuard DNS?
AdGuard DNS is one of the most privacy-oriented DNS services on the market. It supports such reliable encryption protocols as DNS-over-HTTPS, DNS-over-TLS, and DNS-over-QUIC. It can work as a regular DNS resolver in Non-filtering mode, but also it can provide DNS-level content blocking: identify requests to ad, tracking, and/or adult domains (optionally), and respond with an empty response. AdGuard has its own frequently updated database with names of domains that serve ads, trackers, and scam.
About 75% of AdGuard DNS traffic is encrypted. This is actually what differentiates content-blocking DNS servers from others. If you take a look at CloudFlare or Quad9 stats, you’ll see that encrypted DNS is just a small share of all queries.
AdGuard DNS exists in two main forms: Public AdGuard DNS and Private AdGuard DNS. None of these services require the installation of apps. They are easy to set up and use, and provide users with the minimum features necessary to block ads, trackers, malicious websites, and adult content (if required). There are no restrictions on what devices they can be used with.
Despite so many similarities, private AdGuard DNS and public AdGuard DNS are two different products. Their main difference is that you can customize Private AdGuard DNS, while Public AdGuard DNS cannot.
DNS filtering module in AdGuard products
All major AdGuard products, including AdGuard VPN, have a DNS filtering module where you can select a DNS server by a provider you trust. Of course, AdGuard DNS Default, AdGuard DNS Non-filtering and AdGuard DNS Family Protection are on the list. Also, AdGuard apps allow users to easily configure and use AdGuard DNS — Public or Private.