IPs liées
Qu'est-ce qu'une IP liée et pourquoi est-ce utile
Tous les appareils ne prennent pas en charge les protocoles DNS chiffrés. Dans ce cas, vous devez envisager de configurer DNS non crypté. Par exemple, vous pouvez utiliser une adresse IP liée. La seule exigence pour une adresse IP liée est qu'elle doit être une adresse IP résidentielle.
Une adresse IP résidentielle est attribuée à un appareil connecté à un FAI résidentiel. Elle est généralement liée à un emplacement physique et attribuée à des maisons ou appartements individuels. Les gens utilisent des adresses IP résidentielles pour des activités en ligne quotidiennes comme parcourir le Web, envoyer des courriels, utiliser les réseaux sociaux ou diffuser du contenu.
Parfois, une adresse IP résidentielle peut déjà être utilisée, et si vous essayez de vous y connecter, AdGuard DNS empêchera la connexion.
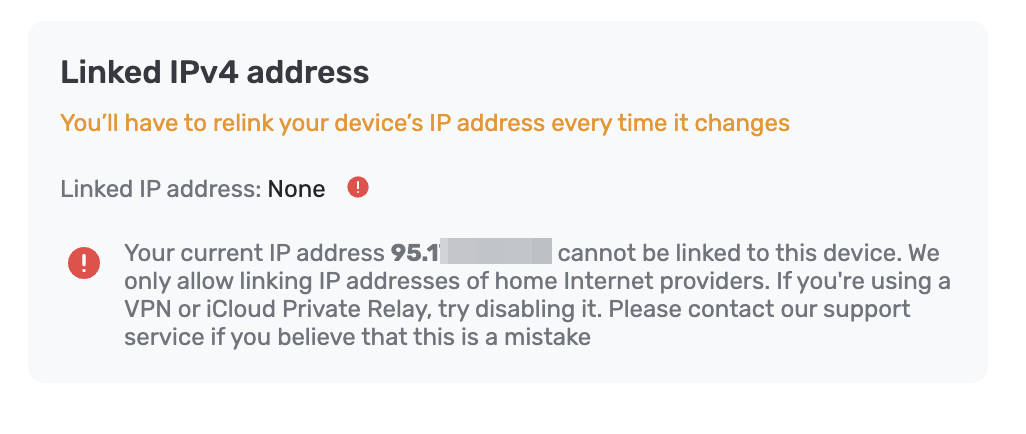
Dans ce cas, veuillez contacter le service d'assistance à l'adresse support@adguard-dns.io, qui vous aidera à définir les paramètres de configuration appropriés.
Comment configurer l'IP liée
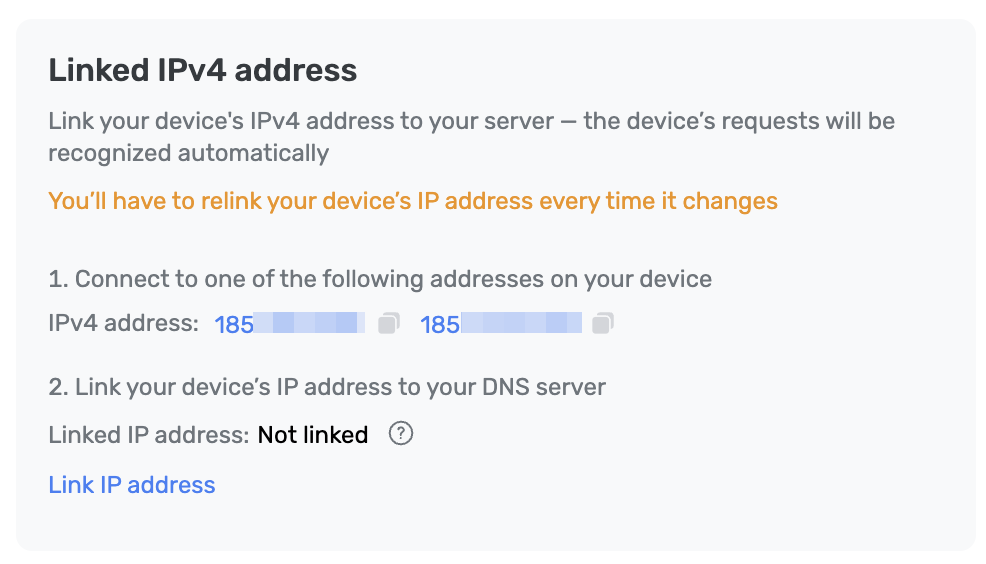
Les instructions suivantes expliquent comment se connecter à l'appareil via l'adresse IP liée :
Ouvrez le tableau de bord.
Ajoutez un nouvel appareil ou ouvrez les paramètres d'un appareil précédemment connecté.
Accédez à Utiliser les adresses des serveurs DNS.
Ouvrez les Adresses des serveurs DNS simples et connectez l'IP liée.
DNS dynamique : Pourquoi c'est utile
Chaque fois qu'un appareil se connecte au réseau, il obtient une nouvelle adresse IP dynamique. Lorsqu'un appareil se déconnecte, le serveur DHCP peut attribuer l'adresse IP libérée à un autre appareil du réseau. Cela signifie que les adresses IP dynamiques changent fréquemment et de manière imprévisible. Par conséquent, vous devrez mettre à jour les paramètres chaque fois que l'appareil est redémarré ou que le réseau change.
Pour garder l'adresse IP liée à jour automatiquement, vous pouvez utiliser DNS. AdGuard DNS vérifiera régulièrement l'adresse IP de votre domaine DDNS et la liera à votre serveur.
Le DNS dynamique (DDNS) est un service qui met automatiquement à jour les enregistrements DNS chaque fois que votre adresse IP change. Il convertit les adresses IP réseau en noms de domaine faciles à lire pour votre confort. Les informations qui relient un nom à une adresse IP sont stockées dans un tableau sur le serveur DNS. Le DDNS met à jour ces enregistrements chaque fois qu'il y a des changements dans les adresses IP.
Ainsi, vous n'aurez pas à mettre à jour l'adresse IP associée manuellement chaque fois qu'elle change.
Le DNS dynamique : Comment le configurer
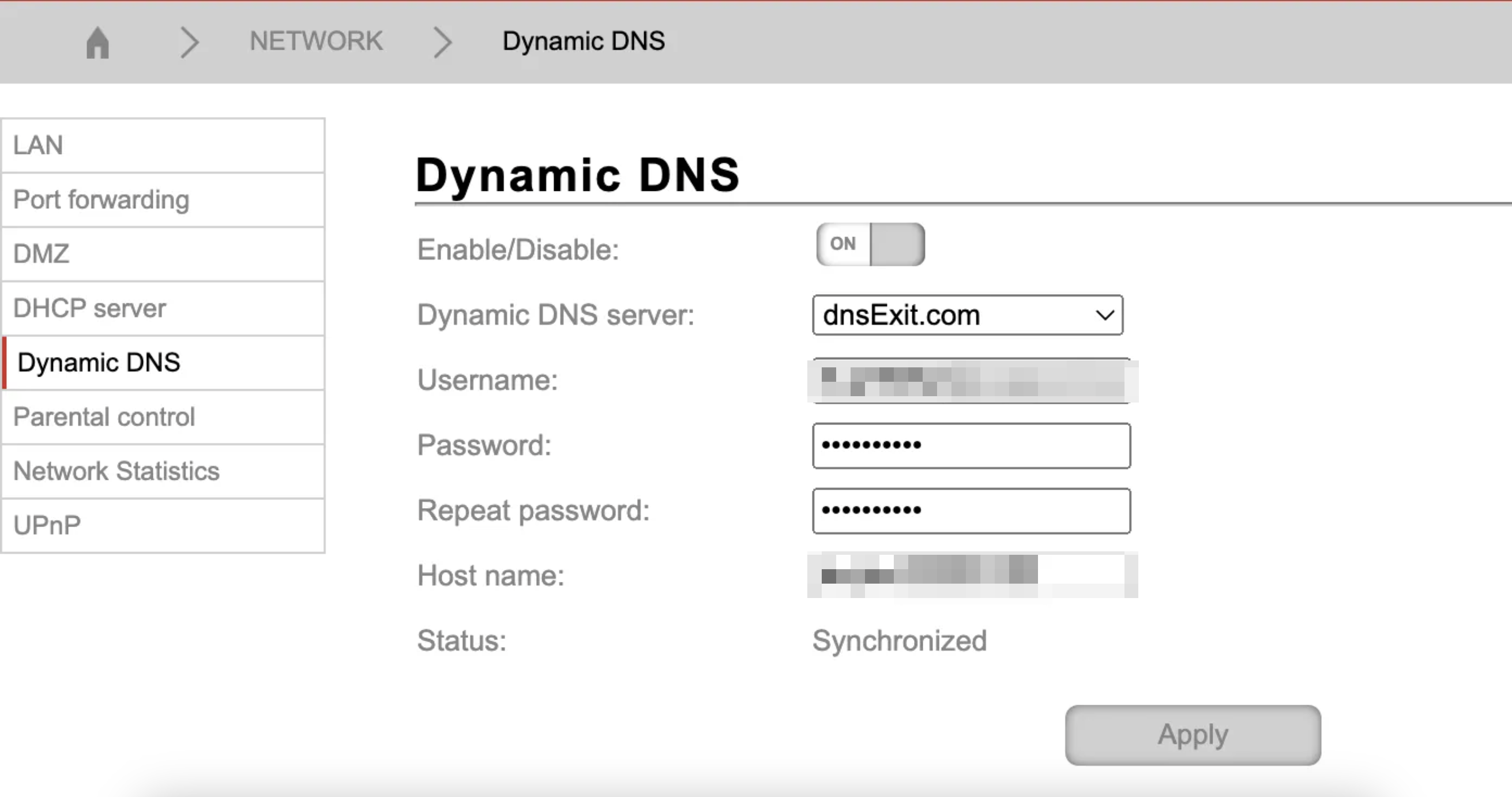
Tout d'abord, vous devez vérifier si DDNS est pris en charge par les paramètres de votre routeur :
- Accédez aux Paramètres du routeur → Réseau
- Trouvez la section DDNS ou DNS dynamique
- Accédez-y et vérifiez que les paramètres sont bien pris en charge. Ce n’est qu’un exemple de ce à quoi cela peut ressembler, les réglages peuvent varier selon votre routeur
Enregistrez votre domaine auprès d'un service populaire comme DynDNS, NO-IP, ou tout autre fournisseur de DDNS de votre choix.
Saisissez le domaine dans les paramètres de votre routeur et synchronisez les configurations.
Accédez aux paramètres IP liés pour connecter l'adresse, puis allez dans Paramètres avancés et cliquez sur Configurer le DDNS.
Saisissez le domaine que vous avez enregistré précédemment et cliquez sur Configurer DDNS.
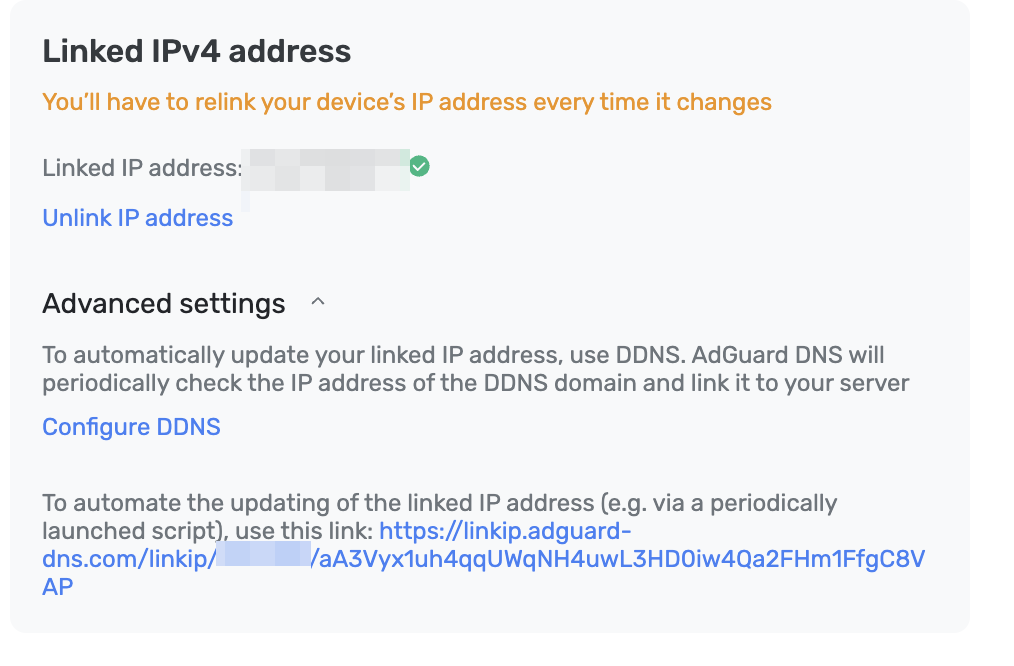
Tout est fait, vous avez réussi à configurer DDNS !
Automatisation de la mise à jour de l'IP liée via script
Sur Windows
La façon la plus simple est d'utiliser le Planificateur de tâches :
- Créez une tâche :
- Ouvrez le Planificateur de tâches.
- Créez une nouvelle tâche.
- Définissez le déclencheur pour qu'il s'exécute toutes les 5 minutes.
- Sélectionnez Exécuter le programme comme action.
- Sélectionnez un programme :
- Dans le champ Programme ou Script, tapez
powershell - Dans le champ Ajouter des arguments, tapez :
Command "Invoke-WebRequest -Uri 'https://linkip.adguard-dns.com/linkip/{ServerID}/{UniqueKey}'"
- Dans le champ Programme ou Script, tapez
- Enregistrez la tâche.
Sur macOS et Linux
Sur macOS et Linux, la façon la plus simple est d'utiliser cron :
- Ouvrez crontab :
- Dans le terminal, exécutez
crontab -e.
- Dans le terminal, exécutez
- Ajoutez une tâche :
- Insérez la ligne suivante :
/5 * * * * curl https://linkip.adguard-dns.com/linkip/{ServerID}/{UniqueKey} - Cette tâche s'exécutera toutes les 5 minutes
- Insérez la ligne suivante :
- Enregistrez crontab.
- Assurez-vous d'avoir
curlinstallé sur macOS et Linux. - N'oubliez pas de copier l'adresse des paramètres et de remplacer
ServerIDetUniqueKey. - Si une logique ou un traitement des résultats de la requête plus complexe est nécessaire, envisagez d'utiliser des scripts (par exemple, Bash, Python) en conjonction avec un planificateur de tâches ou cron.